A Complete Guide to IT Asset Disposition
What is IT asset disposition? Discover how ITAD helps businesses securely manage outdated equipment, protect data, and promote sustainability.
In this article:
- What is ITAD (IT Asset Disposition)?
- Why is ITAD Important?
- What Does IT Asset Disposition Do?
- Six IT Asset Disposition Requirements
- 1. Data Security and Erasure
- 2. Regulatory Compliance
- 3. Environmental Responsibility
- 4. Asset Tracking and Reporting
- 5. Value Recovery and Reuse
- 6. Certified Disposal Partners
- Relationship Between ITAD and Asset Lifecycle Management
- How To Develop an ITAD Policy For Your Business?
- 1. Start with Disposition Planning
- 2. Incorporate Asset Repair and Maintenance
- 3. Establish an Asset Retrieval Process
- 4. Implement Secure Data Destruction
- 5. Determine Disposal Methods: Resell, Donate, or Destroy
- 6. Track, Document, and Report Updates
- 7. Engage Certified Disposal Partners
- Best Practices For Successful IT Asset Disposition
- 1. Prioritize Employee Awareness and Training
- 2. Regularly Assess Your IT Asset Inventory
- 3. Evaluate Asset Retrieval and Disposal Methods
- 4. Track Progress and Maintain Accurate Records
- 5. Stay Up-to-date with Regulations and Industry Standards
- Simplify Your IT Asset Disposition with Itefy

What happens when your company’s old laptops, servers, and devices become outdated? Do they just keep piling up, or is there a better way to manage them? There’s actually a better way, and it’s called IT Asset Disposition (ITAD).
It’s all about properly handling and disposing of unused or outdated IT assets. Whether it’s securely wiping data, recycling, or reselling, ITAD helps businesses stay efficient and eco-friendly. It also ensures that your business safely manages old equipment, follows regulations, and reduces environmental impact.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about IT Asset Disposition. So, let’s dig in.
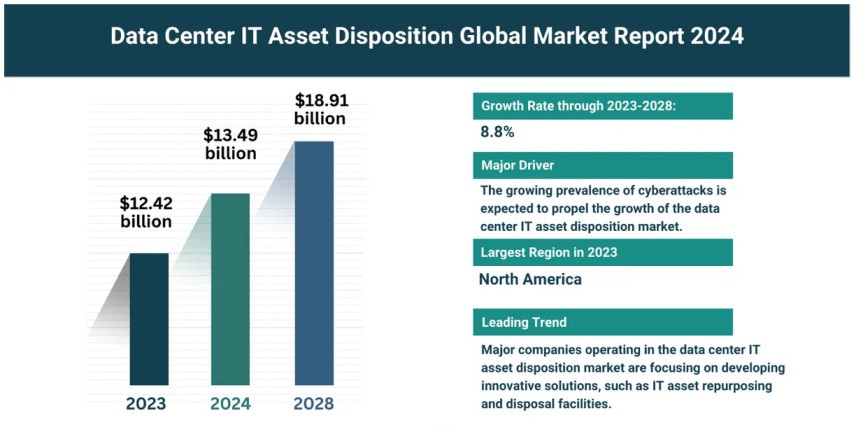
Source: The Business Research Company
What is ITAD (IT Asset Disposition)?
Understanding ITAD's meaning is essential for businesses managing the lifecycle of their IT equipment. IT Asset Disposition refers to the process of securely handling, retiring, and disposing of outdated or unused technology, such as computers, servers, smartphones, and other devices.
The process involves several crucial steps, including auditing assets, securely erasing sensitive data, determining whether the equipment can be refurbished or resold, and ensuring environmentally responsible recycling.
ITAD helps companies recover value from old devices through resale or donation while reducing their environmental impact by minimizing e-waste. Without proper disposal, these assets can accumulate in the environment, damaging the atmosphere. Furthermore, improper disposal can lead to data breaches, expose sensitive information, and cause legal or financial penalties.
According to a 2019 survey, e-waste accounted for 53.6 million metric tons, of which only 17.4% was collected and recycled. This highlights the need for companies to dispose of their assets responsibly.

Source: Shyft Global Services
Why is ITAD Important?
Out of the 53.6 million metric tons of waste mentioned above, 44 million are still sitting somewhere in a landfill, with much more gathered over the years. This is essentially why businesses now need to build a responsible ITAD policy for the proper management of assets.
Another primary reason why it is essential is data security. Old devices often contain sensitive information. If not properly wiped or destroyed, they can lead to data breaches, exposing confidential business and customer information.
Regulatory compliance is also a critical factor in this regard. Many industries have strict regulations around data handling and disposal. Non-compliance with these rules can result in heavy fines. Since the implementation of GDPR, there have been over €4 billion in fines, and you can be the next one if you don’t follow the rules.

Source: Privacy Affairs
Additionally, ITAD offers financial benefits, as businesses can recover value from retired equipment through resale or recycling. Companies can support sustainability efforts by reducing e-waste, which is a growing concern all around the world.
What Does IT Asset Disposition Do?
IT asset disposition is more than just getting rid of outdated equipment. It covers every step involved in handling IT assets from the moment they are no longer needed to their final destination, whether through resale, recycling, or disposal.
Here’s what ITAD does:
- Asset Auditing and Tracking: This process starts by identifying and cataloging all outdated devices. It tracks these assets to ensure nothing is lost or mishandled.
- Data Erasure and Destruction: One of the most critical tasks of information technology asset disposal is ensuring that sensitive data on devices is securely erased.
- Value Recovery Through Resale: This helps businesses determine whether retired equipment can be resold, refurbished, or donated.
Six IT Asset Disposition Requirements
IT asset disposition requires companies to follow specific practices to ensure the secure, compliant, and environmentally responsible disposal of outdated or unwanted technology. Meeting these requirements helps businesses protect data, recover value, and stay compliant with industry regulations. The IT asset disposition requirements include:
1. Data Security and Erasure
One of the top priorities in ITAD is protecting sensitive information. Before any device leaves the company, all data must be securely wiped or destroyed.
Using certified data erasure software or physical destruction methods ensures that no data can be recovered, reducing the risk of data breaches.
2. Regulatory Compliance
When disposing of IT assets, businesses must comply with data protection laws, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or local regulations.
ITAD providers are required to provide documentation and asset management audit trails to show that the disposal process meets these standards, protecting the company from legal penalties.
3. Environmental Responsibility
Do you know that 32% (17.4 MT) of the most common e-waste in 2019 was small equipment, and 24% was large equipment? This is the reason why companies are now made responsible for ensuring that e-waste is minimized.
IT asset disposition requires eco-friendly recycling practices, such as extracting reusable parts or recycling materials safely. These practices help reduce landfill waste and support sustainability goals.
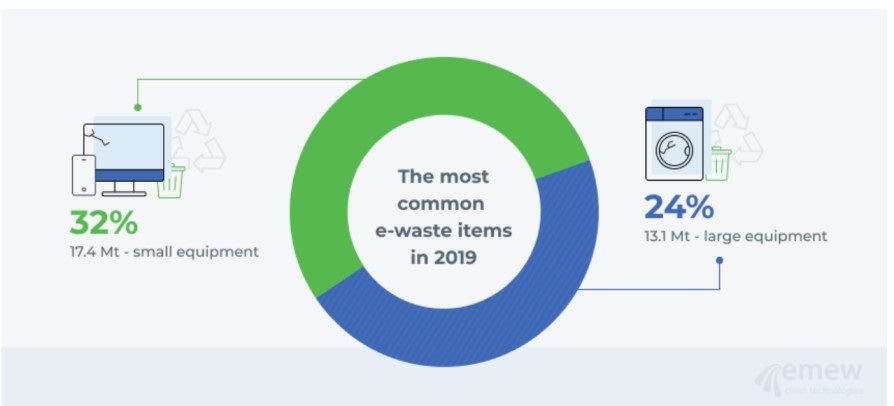
Source: emew clean technologies
4. Asset Tracking and Reporting
A key part of the ITAD process is tracking every asset throughout its disposal journey. This involves detailed asset audits, documenting each device’s condition, and generating reports for transparency. Proper tracking helps businesses stay organized and compliant.
5. Value Recovery and Reuse
Not all retired equipment is obsolete. ITAD requires evaluating whether devices can be resold, refurbished, or donated. This helps companies recover some value from older assets and reduce waste at the same time.
6. Certified Disposal Partners
Working with certified IT asset disposition companies is important. These service providers follow IT asset disposition industry standards like R2 or e-Stewards to ensure secure and environmentally responsible disposal. Partnering with certified professionals gives businesses peace of mind that the entire process is handled correctly.
Relationship Between ITAD and Asset Lifecycle Management
Every piece of IT equipment in a company goes through multiple phases, from acquisition to disposal. This means that IT asset disposition or disposal is a crucial stage within the asset lifecycle management. It plays a major role in managing the later stages of this lifecycle, ensuring that assets are handled properly when they are no longer needed.
One key aspect of ITAD within lifecycle management is asset repair and refurbishment. Devices that initially seem near the end of their useful life may still have the potential for continued use with proper evaluation.
For example, a server with minor issues may be refurbished with minimal effort, allowing it to serve its purpose longer. This helps businesses make better decisions and save some money by choosing repair over replacement when practical.
How To Develop an ITAD Policy For Your Business?
As a business owner, you need to create an effective IT asset disposition policy to manage your company’s outdated and unused It equipment. An ITAD policy provides a clear framework to ensure data security, regulatory compliance, environmental sustainability, and financial accountability.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you develop an ITAD policy for your business.
1. Start with Disposition Planning
Planning is critical to creating a strong ITAD policy. Outline the steps for evaluating IT assets and selecting the appropriate disposal method (repair, recycling, resale, or destruction). Engage the stakeholders early on and identify their roles and responsibilities to ensure alignment.
The planning phase should also include timelines and required resources, which must be approved by your executive team to ensure proper implementation.
Key Considerations for Planning
- Risk Assessment: Conduct a risk assessment to identify potential data, environmental, and regulatory risks.
- Consider ITAD Policy: Align the ITAD policy with your company’s sustainability goals and stakeholder requirements.
- Create Plans for Disruptions: Plan for unexpected disruptions by scheduling asset decommissioning outside peak hours.
2. Incorporate Asset Repair and Maintenance
Before you decide to dispose of IT assets, your ITAD policy should include guidelines for asset repair. Evaluate whether an item is worth repairing based on cost and functionality.
Repairing or refurbishing assets instead of replacing them extend the lifecycle and reduce costs. Include details on service providers and repair criteria in the policy.
3. Establish an Asset Retrieval Process
In this next step, you must outline clear procedures for retrieving and decommissioning IT equipment. Once a device is no longer used, securely remove it from your infrastructure to mitigate risks.
Include instructions for tracking and transporting the equipment to a secure location until it undergoes the next step in the IT asset disposition process.
4. Implement Secure Data Destruction
Based on the data's sensitivity, define the media sanitization techniques to be used. These can include overwriting, degaussing, or physical destruction of storage devices.
Proper data cleaning ensures compliance with data protection laws, such as GDPR and HIPAA, and it prevents unauthorized access to sensitive information.
5. Determine Disposal Methods: Resell, Donate, or Destroy
The policy you’re creating should specify the methods for disposing of IT assets that cannot be repaired. You can include the following options:
- Resell: Resell assets that hold market value to recoup some operational costs.
- Donate: you can offer reusable equipment to schools, charities, or nonprofits.
- Destroy: If none of the above options apply, include a policy for certified destruction. Engage third-party vendors for recycling or shredding material and request disposal certificates to document the process.
6. Track, Document, and Report Updates
Your ITAD policy should emphasize tracking and documentation to hold your company accountable. Record every stage of the disposition process and update the status of each asset in your inventory system.
Make sure software licensees or vendor contracts linked to decommissioned devices are also updated or canceled. Include guidelines for creating detailed reports for audits, financial tracking, and sustainability efforts.
7. Engage Certified Disposal Partners
If your company partners with third-party vendors, the ITAD policy should outline how to evaluate potential service providers. Key aspects to consider here are:
- Government licenses and certifications (e.g., R2, e-Stewards).
- ISO certifications, such as ISO 27001 for information security and ISO 14001 for environmental management.
- Chain of custody documentation and issuance of disposal certificates.
Formal vendor contracts should address all legal, regulatory and security concerns to minimize risks and ensure compliance.
Best Practices For Successful IT Asset Disposition
Here are some best practices to follow to make your IT asset disposition process smooth, secure, and sustainable.
1. Prioritize Employee Awareness and Training
Your employees should be familiar with your ITAD policy and understand their roles within the process. Provide training to staff involved in physical asset management and data handling. Clear communication and training ensure that ITAD procedures are consistently followed, preventing errors that could compromise data security.
2. Regularly Assess Your IT Asset Inventory
Maintain an up-to-date inventory to track the status and condition of your IT assets. Regular monthly or quarterly audits can help identify discrepancies, such as missing records for damaged equipment. Accurate tracing ensures assets are disposed of or repaired promptly.
3. Evaluate Asset Retrieval and Disposal Methods
Assessing the effectiveness of different disposal methods helps optimize your IT asset disposition process. Determine the cost, risk, and environmental impact of repair, resale, donation, and destruction options. You can customize your methods based on your organization's security needs.
4. Track Progress and Maintain Accurate Records
Keep detailed records throughout the process, from asset retrieval to final disposal. Update your asset register to reflect changes and ensure licenses and contracts linked to disposed assets are managed correctly.
5. Stay Up-to-date with Regulations and Industry Standards
ITAD policies must be kept updated according to changing regulations. Regularly review your policy to ensure compliance with laws. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines, data breaches, and reputational damage.
Simplify Your IT Asset Disposition with Itefy
IT asset disposition is essential for organizations to securely handle their outdated equipment, ensuring data protection, regulatory compliance, and sustainability.
This is where Itefy comes in with its Equipment Management tools to transform your asset management process. With a powerful yet easy-to-use platform, Itefy offers complete control over your equipment’s lifecycle. It provides real-time inventory tracking through QR code scanning and mobile access.
With Itefy, you’ll have all the tools you need to optimize asset management. Take the next step and book your free trial today.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
IT assets refer to any hardware, software, or technology resources that a business owns or utilizes. This includes devices like computers, servers, and routers, as well as software applications, licenses, and cloud-based tools. Proper management of IT assets ensures security, efficiency, and compliance throughout their lifecycle.
-
IT asset disposal is a part of the ITAD method, where devices that can’t be reused or recycled are destroyed securely. It involves auditing, securing assets, and using certified practices to ensure proper destruction, prevent data breaches, and ensure compliance with regulations.
-
The ITAD standards include:
Reuse and Recycling: Refurbishing to reduce e-waste.
Data Security: To ensure sensitive data is wiped or destroyed.
Environmental Sustainability: Promotes eco-friendly recycling.
Regulatory Compliance: Follows laws like GDPR and HIPAA.
Third-party Certifications: Accredited by auditors (e.g., R2, e-Stewards)
Chain of Custody: Tracks assets through every stage of disposal. -
IT asset disposition is the process organizations use to securely and responsibly manage the disposal and recycling of outdated IT equipment. Sometimes referred to as IT asset recycling, ITAD encompasses the secure handling resale or eco-friendly recycling of devices to minimize environmental impact, reduce e-waste, and protect sensitive data.
