RFID vs NFC in Asset Management - All You Need to Know
RFID vs NFC is a highly pertinent debate in the asset tracking sector. Learn how they differ and which one’s better for your company in this comprehensive exploration.
In this article:
- RFID - An Overview
- Passive RFID
- Active RFID
- NFC - An Overview
- Active Communication
- Passive Communication
- Basics of NFC Asset Tracking
- Pros of NFC for Asset Tracking
- Web NFC Using Chrome on Android
- Enhanced Efficiency and Accuracy
- Cost Effectiveness
- Advanced Security
- Regulatory Compliance
- Flexible Tracking
- Cons of NFC for Asset Tracking
- Not Ideal for Extensive Data
- Interactions With Metals and Liquids
- Pros of RFID for Asset Tracking
- Provides Good Return on Investment (ROI)
- Helps Create Fixed Asset Registers
- Helps Automate Operations
- Minimizes the Risk of FOD
- Cons of RFID for Asset Tracking
- Infrastructure Requirements
- Security Issues
- High Costs
- Durability Concerns
- Track Your Assets With Itefy

Businesses are always striving to improve asset tracking with the help of the latest technologies. But the problem arises when it's time to pick the right technology that fits your unique needs. That's also the case for companies trying to analyze the RFID vs NFC debate.
The worldwide NFC market will be $34.9 billion by 2025. With this level of popularity, it's important to understand RFID vs NFC, how they differ from each other, help you track assets, and more. This guide intends to provide you with in-depth information on the difference between NFC and RFID, so read on.
RFID - An Overview
Radio Field Identification or RFID uses electromagnetic fields to identify and track equipment through tags. The basic setup of an RFID system includes the following:
- RFID tag
- Reader/Scanner
The RFID tag has a memory chip to store data and an antenna. The scanner reads data from the memory chip while the antenna delivers it.
Today, the global RFID market stands at $15.8 billion and is expected to grow rapidly in the coming years. With such a large market share, you can definitely see RFID tags being used in warehouses to track equipment and assets. These tags can be attached to both moveable and immovable assets to track them in all situations. RFID tags can be read up to 200m (650 feet) and don't have to be in the line of sight of the reader.
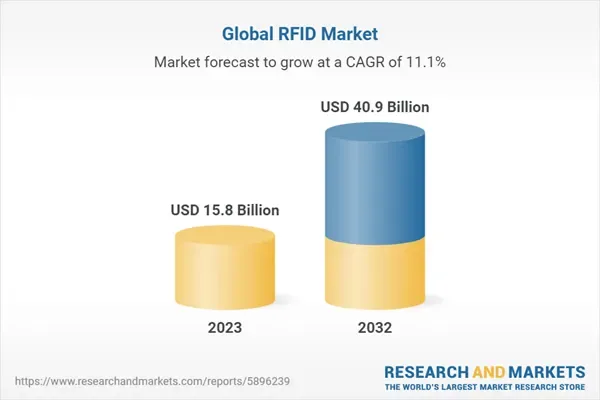
The global RFID market has shown decent growth figures.
The following table details the frequency of various RFID tags and their detection range:
| Frequency Band | Scanning Range |
| 120-150 Hz (Low Frequency, LF) | Up to 10 cm |
| 13.56 MHz (High Frequency, HF) | Up to 1 m |
| 433 MHz (Ultra High Frequency, UHF) | 1-100 m |
| 856-960 MHz (Ultra High Frequency, UHF) | 1-12 m |
| 2450-5800 MHz (Microwave) | 1-2 m (active tags) |
| 3.1-10 GHz (Microwave) | Up to 200 m (active tags) |
Let's also discuss the two types of RFID: Active and Passive RFID.
Passive RFID
Passive RFID tags don't have any battery. They require powerful scanners that send high-power and low-frequency radio waves that are picked by their antenna. It activates the circuitry inside the tag, which then transmits data back to the scanner.
As you might have noticed, it is a unidirectional communication from the tag to the reader. Although it can work for a few meters, passive RFID isn't ideal for asset location management. If you want your passive RFID scanners for location tracking, you'd need them every 10-15 m, which could get prohibitively expensive.
Active RFID
As the name suggests, active RFID tags are battery-powered and can connect to various access points. The data they provide is transferred to RFID software that shows the location of each reader. Active RFID is a better solution for location tracking than passive RFID but still not perfect. For instance, passive RFID only tells you whether a particular item is in the storage room or not. On the contrary, active RFID provides you with real-time locations of all tagged items.
The downside to active RFID is that it requires batteries, which you have to replace after 3-5 years. Passive RFID doesn't need any batteries, so they can theoretically last forever.
NFC - An Overview
Near Field Communication or NFC is wireless personal area network (PAN) technology that enables data transfer between two devices. With just a single tap, people can today transfer data seamlessly between their phones using NFC. For the NFC to function well, both the receiver and the initiator devices must be NFC-enabled. Communication is possible between two NFC-enabled devices even if one is active and the other is passive.
NFC’s adoption has rapidly accelerated in recent years.
Active Communication
In the active NFC communication mode, both the receiver and initiator devices are active. They both have power and can generate fields independently to communicate with each other. To receive data, the active device momentarily deactivates its radio frequency.
Passive Communication
In the passive communication mode, the initiator device supplies the field and the receiver device modulates it. Since the passive device has no power in this mode, it takes the power from the electromagnetic field of the initiator device.
Basics of NFC Asset Tracking
NFC is the leading technology in the fintech world already being used by 5th of the world's population. People use NFC-enabled smartphones to make payments through the ‘tap to pay’ apps. Given the widespread usage and effectiveness of NFC, it's only natural that it is also being used in asset tracking. Data makes it clear that in the RFID vs NFC market size, NFC has a significantly higher number of users.
Smartphones are the most popular types of NFC readers, but there are other scanners available too. Companies fix them in various spots, such as passageways, doors, and vehicles according to their use cases.
NFC Asset tracking means attaching NFC tags to physical assets. It creates a digital connection between these assets and a reliable database that includes information like maintenance history, location, use cases, and much more. Whenever assets are moved through an office or a warehouse, these tags enable the company to read them in real-time and make an accurate assessment of all assets.
Pros of NFC for Asset Tracking
Let's now discuss the benefits of using NFC for asset tracking and understand the RFID vs NFC equation in detail.
Web NFC Using Chrome on Android
Do you know that you can read and write to NFC tags from a web page? Just install Chrome 89+ on your NFC-enabled Android device and you're ready to go.
When you bring NFC-enabled Android devices near an NFC tag, it enables Chrome web pages to read and write. Currently, it supports the NFC Data Exchange Format (NDEF), which is a very basic binary message format, but rapid improvements are happening on this front.
Enhanced Efficiency and Accuracy
NFC tags are a massive step up from traditional asset-tracking mechanisms, even when you consider RFID vs NFC. They have come a long way since NFC was first launched back in 2002. Efficient asset tracking is no longer a luxury but a necessity to stay competitive, and NFC is perfect for it with its data transfer capabilities over short distances.
Since there is no need for manual data entry, NFC tags remove the errors in your data and make it as accurate as possible. Detailed information is recorded in a comprehensive digital database that the authorized employees can access anytime. It helps your company keep tabs on the movement of assets and their location 24/7 with unprecedented precision.
Cost Effectiveness
Implementing advanced NFC tracking systems might sound expensive in the beginning, but the benefits certainly outweigh the costs in the long run. Another good news is that in RFID vs NFC cost, the latter comes on top, making it a no-brainer for companies with limited budgets.
You don't need to buy additional data scanners to import data from NFC tags, a significant difference in the RFID vs NFC analysis. All you need are the good old smartphones and tablets that your company is likely already using. Using a well-understood and reliable infrastructure means you don't need to train your teams on new gadgets, saving money and valuable time simultaneously.
Advanced Security
NFC tags take your asset security to the next level. You can attach them to entrances to warehouses, office storage cabinets, and other rooms. Your security personnel can tap the NFC tag each time they're on a surveillance round and prove that they have indeed been keeping an eye on everything.
To what extent information is extracted from NFC tags depends on a company's policies. For instance, the tapping can open up a big form with several questions, such as the following:
- Was the door locked?
- How many people are currently present in the building?
- Was (particular asset) present when you checked?
These questions ensure that your assets are well-guarded to prevent theft and misplacement.
Regulatory Compliance
NFC tags don't just provide excellent security; they're equally good for ensuring your company stays compliant with all the relevant laws and regulations. For instance, attaching NFC tags to fire extinguishers ensures that they're checked regularly according to the rules and regulations.
Ensuring compliance with NFC tags is a streamlined process. Whenever the relevant employee taps an NFC tag, you can show them a compliance checklist containing all the critical procedures that they must perform. This list should also record the date, time, and name of the employee to provide management with a reliable compliance dataset.
Flexible Tracking
NFC tags are the most flexible tracking tools you can find today. No matter what kind of equipment, from machinery to IT devices to office furniture, NFC tags can be easily attached to them. Their versatility allows organizations of all kinds to meet specific requirements and accommodate all kinds of assets.
Cons of NFC for Asset Tracking
NFC has a few downsides, which we'll discuss here.
Not Ideal for Extensive Data
NFC does indeed store a significant amount of data compared to barcodes, but it might still not be enough for some companies that require extensive data points. For instance, if a firm wants to track complex machinery with detailed operating parameters, sensor data, and maintenance logs, it'll require an extensive network of NFC to cover every aspect. It is doable but might be a little inconvenient for some companies.
Interactions With Metals and Liquids
Environmental factors like liquids and metals can interfere with the functioning of NFC tags. Metal surfaces disrupt the radio waves used for communication, ultimately affecting the tag readability. Since some assets are stored in metal containers and shelves, tracking them with NFC could be problematic.
Assets that are either submerged in water or exposed to other liquids are also hard to track because liquids also hamper NFC detection.
Pros of RFID for Asset Tracking
Provides Good Return on Investment (ROI)
Installing RFID means you're getting a lot of value for your money, which directly translates to a high return on investment. It is a relatively cheap system, which means most companies can install it to track their assets. RFID is also a long-lasting solution compared to many other tracking tools, which is why it has helped several businesses in manufacturing and logistics without exceeding budgetary limits.
Helps Create Fixed Asset Registers
RFID is also suitable for creating fixed asset registers. It requires attaching RFID tags to your equipment and creating a digital profile for each.
Each profile holds a treasure of information about the fixed asset you want to track, including:
- Purchasing date
- Original cost
- Warranty and insurance details
Since RFID has extensive storage capabilities, you can even upload pictures of your assets for easier identification. Uploading the instruction manuals for various equipment is also helpful, as you can access it anytime you need it.
Helps Automate Operations
Another benefit of using RFID tracking is that it helps automate various operations, which means assigning tools and equipment to various users. No need to fill loads of paper anymore and waste valuable time - just select the right tools for the right person and assign them instantly with RFID.
Automation also means issue-reporting becomes incredibly easier. For instance, if a machine develops an issue, RFID tags help you report it swiftly, leaving a note to tell others what went wrong.
Minimizes the Risk of FOD
Foreign object damage (FOD) is a serious issue faced by several companies. Some industries that regularly face this issue include construction, aerospace, pharmaceuticals, and industrial manufacturing.
For instance, if a staff member has left a wrench in an engine during maintenance, RFID tags can instantly track it to eliminate the risk of mishaps. The manager can account for all the tools and ensure that they are returned after the completion of maintenance.
Cons of RFID for Asset Tracking
Infrastructure Requirements
RFID tags require an extensive setup including readers, tags, inventory management system, and wiring. All elements must be integrated for the system to work perfectly, which requires a lot of time and money. Sometimes, a particular software being used isn't capable enough and needs to be replaced entirely to align with the new RFID tags, which leads to additional costs.
Security Issues
When you consider RFID vs NFC systems, the former are susceptible to hacking, which can be crippling for companies. Although updating their data improves security, they are still not perfect. Some companies scan RFID tags with cell phones at close range and later copy that data to another tag, which can create security vulnerabilities.
High Costs
Despite offering a satisfactory return on investment, RFID tags can still be prohibitively expensive, especially for small-scale businesses. The hike in bills is especially felt during expansion, which requires additional investments in tags and scanners. In the RFID vs NFC cost analysis, the former lags behind significantly.
Durability Concerns
RFID tags are not well-known to take a beating in harsh manufacturing environments where they're exposed to heat and other abrasive factors. RFID tags contain an antenna and a receiver. Structurally, they're too tiny to withstand a substantial impact in the form of smashing, bending, and the like. Therefore, they're not the ideal options if you want a tough asset-tracking solution.
Track Your Assets With Itefy
Both RFID and NFC tracking systems are being used extensively in various industries, but RFID vs NFC suggests that NFC takes the lead. It is a more modern and sophisticated technology that has seen several improvements over the years and continues to impress with its efficacy and minimal costs.
If you also want to make the most of NFC tracking after knowing the NFC RFID difference, Itefy’s Asset Management System is your best friend. Organize your assets, track and maintain them, and prevent theft. Our advanced tracking system also provides valuable insights to make your company more productive and your assets more robust.
Get in touch with us today and enjoy a 14-day free trial before you pick a package of your choice.
