Top 8 Warehouse Storage Systems for Improved Operations
This guide will help you optimize your warehouse storage. Learn about different storage systems, such as pallet racking, mobile shelving, and mezzanine flooring.
In this article:
- What is a Warehouse Storage System?
- Pallet Warehouse Storage Ideas
- Selective Pallet Racking
- Pallet Flow Storage
- Mobile Shelving
- Drive-in and Drive-thru Pallet Racks
- Push-back Storage System
- Additional Warehouse Storage Solutions
- Cantilever Racks
- Mezzanine Flooring
- Vertical Lift Module (VLM)
- Warehouse Storage Cost
- Monthly:
- Annual:
- Conclusion

A well-managed inventory is at the heart of any successful business, ensuring a seamless flow of goods from production to delivery. Warehouse storage is something that you should not take lightly. Any friction or hindrance causes disruptions throughout the supply chain, making customers unhappy and tanking your sales.
So, how do you organize inventory in your warehouse? There is no one answer to this question, as there are more inventory storage systems than ever. That’s why we are here to help you understand all the popular storage systems, their advantages, and their drawbacks.
Read on to understand all the important details.
What is a Warehouse Storage System?
A warehouse storage system is a comprehensive approach to organizing and storing inventory. It involves using physical structures, software, and processes to optimize space utilization, improve order efficiency, and ensure the safety and security of stored goods. Around 36% of warehouses report insufficient space for inventory, which means an increasing need for robust storage solutions.

The average warehouse size has increased significantly over the years.
Source: Scott Max
If we focus entirely on the physical aspect of warehouse storage, racking is usually divided into two categories: compact and direct systems.
- The compact system is ideal when storing several materials and needing adequate space. Pallet and drive-in-drive-thru racks are prominent examples of this system.
- Direct racks, such as cantilever racks, pallet racks, and mobile racking systems, are the way to go to simplify order picking and ensure complete access.
Picking warehouse storage solutions depends on factors like the total space available, the number of items you store, and whether you need items frequently.
By implementing a well-designed storage system, businesses can significantly enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and improve overall customer satisfaction.
Pallet Warehouse Storage Ideas
Selective Pallet Racking
A selective pallet storage system allows workers to access every pallet in the warehouse. It is ideal for companies storing different types of products or those with high SKU numbers (a high demand for products).
This system stores pallets in single-deep rows, and operators can access any pallet without moving others. Forklifts can access pallets from the front, back, or sides. It consists of upright frames and horizontal beams that create individual pallet storages.
This system is highly adaptable to various inventory needs, making it suitable for various industries, including manufacturing, retail, and logistics.
System Limitations
- Compared to compact storage systems like drive-in/drive-thru or push-back racking, selective racking requires more floor space to store the same amount of inventory.
- The maximum storage height is limited by the reach of forklifts, which can impact the overall storage capacity of the warehouse.
Pallet Flow Storage
Pallet flow storage, also known as flow rack warehouse storage, is a system that uses gravity and rollers to move pallets on a storage module. The number of pallets in this system can range from 2 to 20, providing a deeper storage capacity than many other systems.
It's particularly well-suited for industries with high-volume, low-SKU inventories that require a First-In, First-Out (FIFO) inventory management system.
As the name suggests, this system flows pallets from one end to the other using wheel tracks, pallet flow rails, or full-width rollers. Operators place the pallet on one end, which moves towards the other due to gravity.
Speed controllers are placed in their way to ensure pallets reach the unloading point safely. Operators keep placing the pallets on the first end and moving towards the other until the lane is fully stacked.
System Limitations
- Once a pallet flow lane is dedicated to a specific product, changing its configuration or accommodating different pallet sizes or weights becomes difficult. This lack of flexibility can hinder adaptability to changing inventory needs or seasonal fluctuations.
- If pallets are not loaded correctly or the flow lanes are improperly maintained, they may collide or become jammed. It can often result in product damage or system malfunctions.
Mobile Shelving
Mobile shelving warehouse storage is an ideal option to save floor space. These shelves have low-friction wheels attached to them at the bottom. When placed on floor-mounted tracks or rails, they glide along the surface with minimal resistance, making it easier to move racks across the warehouse. When an aisle is not needed, the units can be closed together, significantly reducing the floor space required for storage.
Since mobile shelving eliminates unnecessary aisles, it can double or even triple the storage capacity within a given space. These systems can lower building costs and energy consumption by reducing the need for extensive floor space.
Furthermore, they can enhance security by allowing controlled access to stored items. Mobile shelving systems are also highly customizable, accommodating various storage needs and adapting to changing requirements.
System Limitations
- While mobile shelving systems provide efficient access to specific rows of shelves, they can limit overall accessibility compared to traditional fixed shelving systems.
- Frequent movement of shelving units can also disrupt workflow and increase the time required to locate and retrieve items.
- The initial investment cost is another major drawback. Its specialized equipment, installation, and potential customization can be pretty expensive.
Drive-in and Drive-thru Pallet Racks
Both drive-in and drive-thru warehouse storage systems use uprights and rail beams, with the former providing vertical support and the latter offering dense pallet storage.
In a drive-in racking system, forklifts navigate through internal lanes to load and unload pallets. Pallets are stored in multiple levels deep within each lane. This system operates on a Last-In, First-Out (LIFO) principle, meaning the last pallet loaded is the first one retrieved.
Drive-in racking is ideal for storing bulk items that don't require frequent rotation, such as seasonal goods or slow-moving products.
Drive-thru racking is similar to drive-in racking but allows loading and unloading from opposite ends of the lane.
It enables a First-In, First-Out (FIFO) inventory management system, ensuring that older pallets are retrieved first. Drive-thru racking is well-suited for products with expiration dates or needing to be rotated regularly.
These systems maximize storage capacity by eliminating aisle space, leading to a more efficient use of warehouse space. Additionally, they can be a cost-effective solution as they reduce the need for extensive racking infrastructure. These systems can improve warehouse productivity by streamlining the loading and unloading process.
System Limitations
- They may not be ideal for warehouses with a diverse product range.
- Accessing specific pallets can be time-consuming and may require moving other pallets, potentially disrupting the storage order.
- Individual pallets' storage depth and limited visibility might make inventory management more complex.
Push-back Storage System
The push-back racking warehouse storage system stores pallets on either side of the aisle at a depth of 2-6 feet. This setting offers more storage density than many other pallet storage techniques. It operates on the Last-In, First-Out (LIFO) principle.
To load a pallet, a forklift places it on the top cart in the bay. As subsequent pallets are added, the forklift pushes the previous pallets back along the inclined rails. This process continues until the bay is full, with the oldest pallet resting at the back. When retrieving a pallet, the forklift removes the frontmost pallet, and the remaining pallets automatically slide forward.
One major advantage of the push-back storage system is that it requires very little maintenance. Since forklifts don’t really enter the system, uprights encounter minimal damage.
The roller and shuttle systems used in these systems are designed to withstand low temperatures without compromising their performance or durability. It allows for efficient storage and retrieval of goods in cold storage facilities, where maintaining product quality is crucial.
Additionally, push-back racking systems' high compaction helps to optimize space utilization in these environments, which can be particularly valuable in cold storage facilities where space is often limited.
System Limitations
- One major disadvantage of this system is that only the front pallets are readily accessible.
- A push-back system isn’t ideal for products with expiration dates or seasonal variations because it follows the FILO method.
- The high-density nature of push-back racking can make it difficult to accommodate different product sizes and weights.
Additional Warehouse Storage Solutions
Cantilever Racks
If you want to store bulky and long materials, a cantilever warehouse storage system is often considered the best choice. Unlike traditional pallet racking with vertical uprights and horizontal beams, cantilever racks feature upright columns with horizontal arms extending outwards. These arms provide support for the stored goods and allow you to access inventory from both sides.
One of the primary advantages of cantilever racking is its versatility. It can accommodate a wide range of products, including lumber, pipes, metal bars, and sheet goods. The adjustable arms can be configured to suit various load sizes and weights, making it a flexible solution for various storage needs.
System Limitations
- The increased cost is due to the specialized design and construction of cantilever racks and the use of heavy-duty materials.
- It is not ideal for storing a wide variety of products, as it is primarily designed for long, bulky items.
- The open design of cantilever racks can make them more prone to damage from accidental impacts or mishandling.
Mezzanine Flooring
A mezzanine flooring system consists of an additional floor that workers build between the ceiling and the original floor. The steel structures in this system are usually free-standing, meaning you can undo them anytime you like.
Depending on requirements, industrial warehouses typically use stainless or carbon steel, wood-finished, laminated, resin, or concrete flooring.
Every warehouse has some unused vertical space that mezzanine flooring aims to utilize. Once it is constructed, workers can access the space below it for various purposes.
Mezzanine warehouse storage is divided into three types:
- Free Standing Mezzanine: As the name suggests, these use specially built structural columns instead of relying on the building's existing structural components.
- Catwalk Mezzanine: This type of mezzanine is typically narrower and less structurally robust than a full-fledged mezzanine. It is designed to create elevated walkways or platforms for workers to access different areas of a facility, such as high shelves or specific workstations.
- Shelving Mezzanine: This type of support system uses existing shelves or racks. It's best suited for applications where the primary purpose is to create additional storage space above existing inventory.
System Limitations
- Mezzanine flooring reduces the ceiling height, which can restrict the storage of tall items.
- Improper installation or overloading of the mezzanine can lead to structural issues, compromising the safety of workers and the integrity of the stored goods.
- The weight of the mezzanine structure, stored goods, and workers add significant load to the existing floor, potentially requiring reinforcement and increasing construction costs.
Vertical Lift Module (VLM)
A vertical lift module is one of the most advanced warehouse storage solutions. It utilizes the vertical space inside a warehouse and stores goods in multiple trays with an extractor mechanism that runs both vertically and horizontally. The use of automated warehouse storage systems is increasing as the warehouse automation market gears up to hit $95.45 billion by 2034.

The warehouse automation market is growing fast.
Source: Scott Max
This system contains several trays stacked on top of each other in vertical arrays. Whenever a worker wants to extract a particular item, VLM’s automated picker locates that tray. Instead of the worker having to move around, the tray itself arrives at the retrieval point from where the item is easily picked.
Its major advantage is automated item retrieval, which helps workers save a lot of their valuable time. Another plus point of this system is the utilization of vertical space that is often left unaddressed in many warehouses.
System Limitations
- They are complex machines that require regular maintenance and potential repairs. This can add to ongoing operational costs.
- VLMs are best suited for storing smaller items. Larger or heavier items may not be suitable for storage in a VLM.
- These systems use electricity, so any power outages or system failures can disrupt operations.
Warehouse Storage Cost
Before we understand the costs of a warehouse, it is crucial to know about its various components:
- Space needed in square feet
- Monthly or annual rent
- Estimated operating expenses, known as Triple Nets (NNN), Net Net Net (NNN), or Common Area Maintenance (CAM)
Let’s calculate how much you can expect to pay on a monthly or annual basis for 5,000 sq feet of space:
Monthly:
- Rental Rate: $0.67 per month
- NNN/CAM Rate: $0.33 per month
- Total Costs: $5,000 per month
Annual:
- Rental rate: $8.00 per year
- NNN/CAM Rate: $4.00 per year
- Total Costs: $60,000 per year
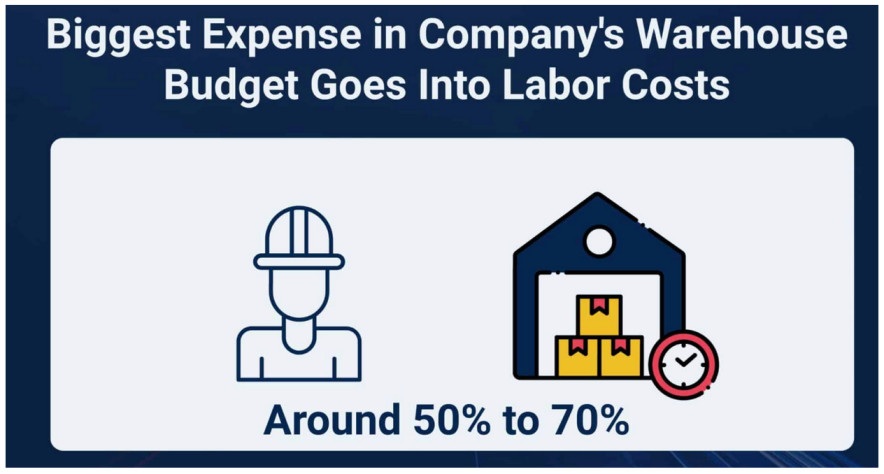
Labor is often the biggest cost for warehouses.
Source: Scott Max
Although the warehouse storage cost has turned out to be the same for both monthly and annual schedules, you are likely to get a discount from the landlord if you pay the total annual costs at once. It is important to note here that labor is often the highest cost for a warehouse, responsible for 50-70% of the total expenses.
Conclusion
Choosing the right warehouse storage system is crucial for maximizing space utilization, improving efficiency, and reducing costs. This article has explored eight popular storage solutions, each with its own advantages and limitations. By understanding your warehouse operation's specific needs, you can make an informed decision about which system best fits you.
Here's where Itefy comes in. As a leading provider of equipment management software, Itefy can help you streamline your storage management process. Our software gives you real-time visibility into your inventory levels and locations, optimizes warehouse layouts, improves picking efficiency, and reduces operational costs by optimizing space usage.
Try our 14-day trial and later upgrade to a paid bundle that suits your needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
If you want to build a 10,000-square-foot warehouse, expect to spend between $350,000 and $500,000. These are estimates; the exact expenditure depends upon the design, materials, size, customizations, and other factors.
-
Warehousing or storage cost refers to all the expenses incurred when you store inventory in a warehouse, such as utilities, insurance, maintenance, labor, rent, and the rest.
-
The main purpose of warehouse storage planning is to maximize the potential of the space you rent or own. It also involves using advanced hardware and software systems to ensure that your inventory is stored productively.
-
You can maximize storage in a warehouse by using a reliable inventory storage system and training your team on using it effectively. It is ideal to combine these methods with reliable inventory management software like Itefy’s to stay notified about every little change in the inventory.
-
The five major types of warehouse storage are:
Pallet racking system
Mobile shelving
Mezzanine flooring
Cantilever racks
Vertical lift module
